Search Results for: protein domain
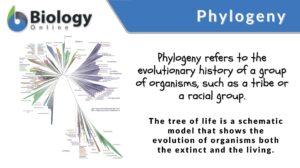
Protein domain
Definition noun (1) An autonomously folding functional unit of a protein. (2) A part of protein that can fold, function... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Integral membrane protein
Definition noun A protein molecule (or assembly of proteins) that is permanently attached or firmly anchored in the plasma... Read More
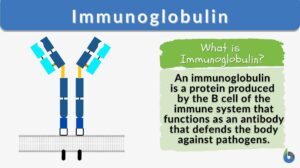
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
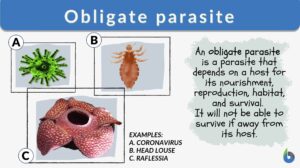
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
Fibronectin
Fibronectin (Science: protein) glycoprotein of high molecular weight (2 chains each of 250 kd linked by disulphide bonds)... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
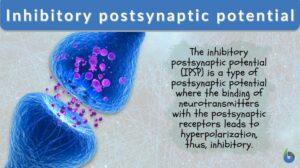
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Transactivation
Definition noun, plural: transactivations (molecular biology, genetics) The stimulation of transcription by expressing an... Read More
Vibrio cholerae
Definition Noun A gram-negative single polar flagellum bacterium associated with cholera infection in... Read More